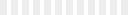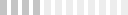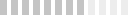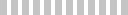Analyzing the Degradation Process of Quantum-Dot LEDs (QLEDs) by Mass Spectrometry
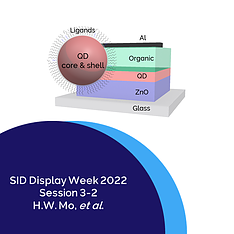
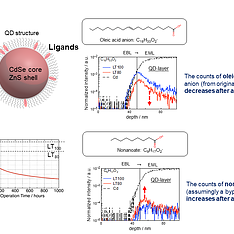
By utilizing time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry (TOF-SIMS), the degradation processes of quantum dot core components and the surface ligands were studied. Intentionally degraded QLED samples were prepared, and the TOF-SIMS mass composition signals of each layer within the QLEDs are estimated. The result of the analysis gives possible structural information of the degraded species induced in the device, providing useful insights for further developments of highly efficient R/G/B quantum dot materials.
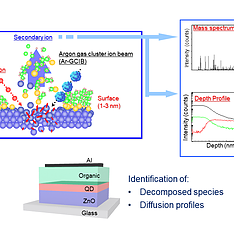
In this report, we demonstrated depth profiling analyses of pristine and degraded (both EL- and PL-aged) QLEDs by a GCIB-TOF-SIMS. According to the profile at the HTL/EML interface, it was possible to sort out which components within the emitting quantum dot are not endurable against an electrical operation. The TOF-SIMS analysis of the PL-degraded sample suggested more complex channels of the ligand decomposition. We believe that this analytical method can support researchers to solve the critical issue (such as cadmium diffusion) and to explore potential shell and ligand combinations for ensuring a stable QD stoichiometry. We thus hope that this methodology can widen further possibilities for QLED materials development.